What Are Life Processes?
Life processes are basic biological functions that every living organism performs to stay alive.
These biological functions explain that what is life process and how it functions in living things, including both plants and animals.
The 7 Essential Life Processes
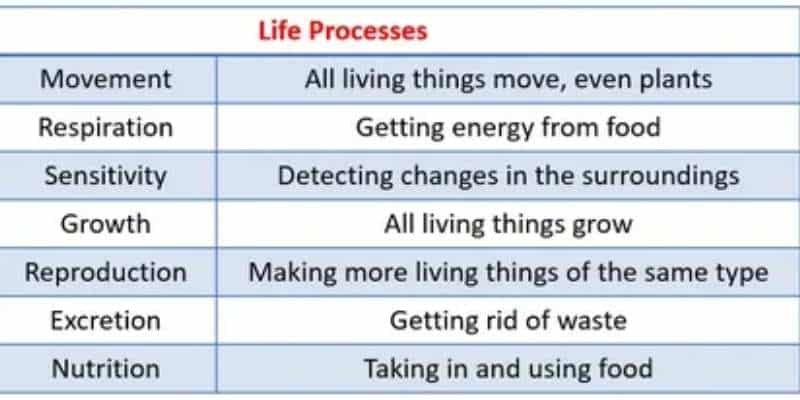
In every living organism,, the following 7 life processes must take place:
- Movement
- Respiration
- Sensitivity (Response to stimuli)
- Growth
- Reproduction
- Excretion
- Nutrition
Let’s discuss these in detail!
1. Movement
What is it?
It defines the ability of an organism to change its position or any part of its body.
Examples
- Animals move their whole bodies , like by walking, swimming, flying.
- Plants do not walk, but they move parts slowly, like turning leaves toward sunlight or opening flowers.
Why is it important?
- Movement helps animals find food, shelter, and escape from danger.
- Helps plants to maximize photosynthesis by facing the Sun.
Respiration
What is it?
Respiration is the process of breaking down food to release energy. All the other processes of life are accomplished by the use of this energy.
Types of respiration
- Aerobic respiration – uses oxygen
- Anaerobic respiration – does not use oxygen (e.g., yeast)
Examples
- Glucose and oxygen react to generate energy (ATP), carbon dioxide, and water in human beings.
- Plants also breathe as they utilize the glucose which has been produced through photosynthesis in order to produce energy.
Why is it important?
Energy from respiration powers muscle movement, cell repair, thinking, digestion, and everything!
Sensitivity (Response to Stimuli)
What is it?
Sensitivity is the ability to detect and respond to changes in the environment. The changes are referred to as stimuli.
Examples
- Human beings respond to high temperatures through sweating.
- Lights cause the bending of plants towards them (phototropism).
- When a dog hears a loud noise, he/she run.
Why is it important?
- It helps to keep organisms protected, locate food, and survive.
- The responses may be fast (animals) or slow (plants).
Growth
What is it?
Growth refers to an increment of size and mass of an organism with time.
The way it occurs:
- It grows by dividing cells.
- In animals, growth tends to end at adulthood.
In plants, the growth does not cease during the life span (especially in the roots and shoots).
Examples
- An infant becoming a man.
- It is the sprouting of a seed into a tree.
Why is it important?
Increase heals and builds tissues, builds strength and makes possible reproduction.
Reproduction
What is it?
Reproduction is the process by which organisms produce new individuals of the same species.
Types of reproduction:
- Sexual – involves two parents (e.g. humans, animals)
- Asexual – involves one parent (e.g. bacteria, some plants)
Examples
- Humans reproduce by sexual reproduction.
- Strawberry plants use runners for asexual reproduction.
Why is it important?
- Keeps the species from going extinct.
- Even though not essential for an individual’s survival, it’s critical for life to continue.
Excretion
What is it?
Excretion is the process of removing waste products formed inside the body during metabolism.
Examples:
- Humans excrete urea in urine, carbon dioxide in breath, and sweat.
- Plants get rid of oxygen during the day and shed old leaves to remove waste.
Why is it important?
- Waste like CO₂ and urea is harmful if not removed.
- Maintains a clean internal environment in the body.
Nutrition
What is it?
Nutrition is the process of taking in food and using it for energy, growth, and repair.
Types of nutrition:
- Autotrophic – Organisms like plants make their own food (photosynthesis).
- Heterotrophic – Organisms like animals eat other organisms.
Examples:
- Plants use sunlight, CO₂, and water to create glucose (sugar).
- Animals eat plants or other animals for energy.
Why is it important?
- Provides the fuel the body needs to carry out all other life processes.
Plant vs. Animal Life Processes
| Process | Plants | Animals |
| Nutrition | Autotrophic — make food through photosynthesis | Heterotrophic — depend on other organisms for food |
| Movement | Show slow growth movements (tropisms) | Active movement using muscles and body parts |
| Respiration | Cellular respiration; photosynthesis releases oxygen | Respire with oxygen and release carbon dioxide |
| Sensitivity | Respond slowly through hormones | Quick response via nervous system |
| Growth | Grow continuously at meristem regions | Grow only up to a certain age or size |
| Reproduction | Sexual (seeds) and asexual (spores, cuttings) | Mainly sexual reproduction, few asexual cases |
| Excretion | Through stomata, vacuoles, and shedding leaves | Kidneys, lungs, and skin remove waste |
What is a life process in simple words?
A life process is something a living thing does to stay alive. This includes eating, breathing, growing, or getting rid of waste.
What are the 7 life processes of living things?
The seven life processes are movement, respiration, sensitivity, growth, reproduction, excretion, and nutrition. Together, they are remembered as MRS GREN.
How do living things get their food?
Plants make their own food using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide through a process called photosynthesis. Animals get their food by eating plants or other animals.
What is the difference between plant and animal life processes?
Plants stay in one place and make their own food. They grow all the time and get rid of waste in different ways. Animals move around, eat food from other sources, and have more complex ways to feel things and remove waste.
What are some examples of biological processes?
Biological processes include the seven life processes. Some other examples are photosynthesis, digestion, metabolism, cell division, and keeping the body balanced, which is called homeostasis.